ERP data systems are the backbone of all but the smallest companies. At the core of an ERP system is the “general ledger” or accounting system that tracks all of a company’s financial aspects – and virtually everything has an impact on your financials. Marketing and selling a product has an impact; purchasing raw materials from a vendor has an impact; designing, manufacturing, and storing products has an impact; and, last but not least, hiring and paying employees will have an impact on financials.
Companies often choose to implement an ERP system for one of two reasons:
- To achieve real-time visibility of the entire business in a single application. Because data from all parts of the organization are managed and consolidated in the ERP system, you gain complete transparency of your business performance at any moment of time.
- To increase efficiency due to business process integration. Running all parts of your business in a single system provides huge advantages, because you don’t need to key data into multiple systems of record. Intermediate data from one step in a business process are available for the next step.
Although an ERP data system is essential to operating and scaling a company, it often comes with multiple challenges that include:
- Too much data to input. To accurately track everything so your business can run better and you can access the reports you need, the ERP system requires vast amounts of data. Entering data in a timely and accurate manner ultimately becomes the responsibility of ERP end users. But the process of collecting data that needs to be fed into the ERP system and then entering data is often manual, time-consuming, and error-prone.
- Difficult to use. Due to the amount of data needed and the number of screens users have to navigate, ERP systems are notoriously difficult to use. ERP users need to be continually trained to use the system effectively, and unfortunately due to budget constraints, end-user training falls by the wayside too frequently.
- Difficult and expensive to change and adapt. Adapting your ERP system processes to your business frequently involves customizing your ERP system. This is an expensive and time-consuming proposition that consumes valuable programming resources.
Because of these challenges, ERP systems often do not live up their promise of delivering efficient operations and real-time accurate reporting. In addition, data in ERP systems is often poor quality and untrustworthy. Compounding these problems and the manual processes that feed data into the system results in increased cycle times for all business activities.
Read the eBook
How to Tackle the Top 3 Challenges with Materials and SAP Product Data
This eBook provides practical tips on how to tackle the top 3 product data challenges in your manufacturing processes and real-world examples of the results you can achieve by deploying smart, fit-for-purpose automation solutions.
To accurately track all activities so your business can run efficiently and report accurately, the ERP system requires vast amounts of data. Every step in a business process requires users to enter or update data in an ERP system. Entering data in a timely and accurate manner becomes the responsibility of ERP end-users. Sometimes data that is entered into ERP has to be collected from other people inside or outside the organization, such as invoices from vendors. This process of collecting data that needs to be fed into the ERP system and then entering data in is often manual, time-consuming, and error-prone.
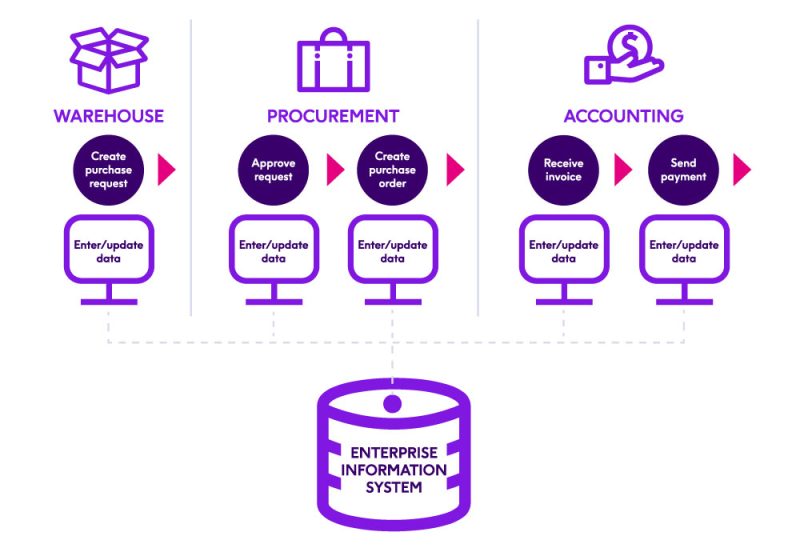
Because the ERP system supports end-to-end processes, more data is needed to ensure accuracy. For example, to create a customer record in ERP, you not only need to create the financial part of the customer record, but also the sales part, the warehouse part, the marketing part, etc. The more data that needs to be entered, the greater risk you run for mistakes. These mistakes, unfortunately, won’t often show up until much later in the process.
These manual, error-prone steps lie at the root of many data quality issues in the enterprise. Because every process has a financial impact, all data quality issues eventually flow down to the accounting team. A minor data issue in the beginning of the process snowballs by the time it gets to the end of the process where it can become a massive problem. In many organizations, it then becomes the accounting team’s responsibility to resolve the problem caused by upstream data quality issues.
At the end of the day, data problems in ERP are not really the result of how the ERP system is architected or configured. They’re often caused by a lack of user training or business process engineering. The ERP system increases the size and complexity of the problem because everything is tied together.
Read our eBook How to Tackle the Top 3 Challenges with Materials and SAP Product Data which provides practical tips on how to tackle the top 3 product data challenges in your manufacturing processes and real-world examples of the results you can achieve by deploying smart, fit-for-purpose automation solutions.







